Watch a vodcast on crystal deposition in various organs
Associated gout comorbidities
Comorbidities are common in patients with gout, according to the 2007–2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data4
74%
had hypertension
71%
had stage 2* or greater chronic kidney disease
53%
were obese†
26%
had diabetes
14%
had a history of myocardial infarction
10%
had a history of stroke
*eGFR >60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
†>30 kg/m2.
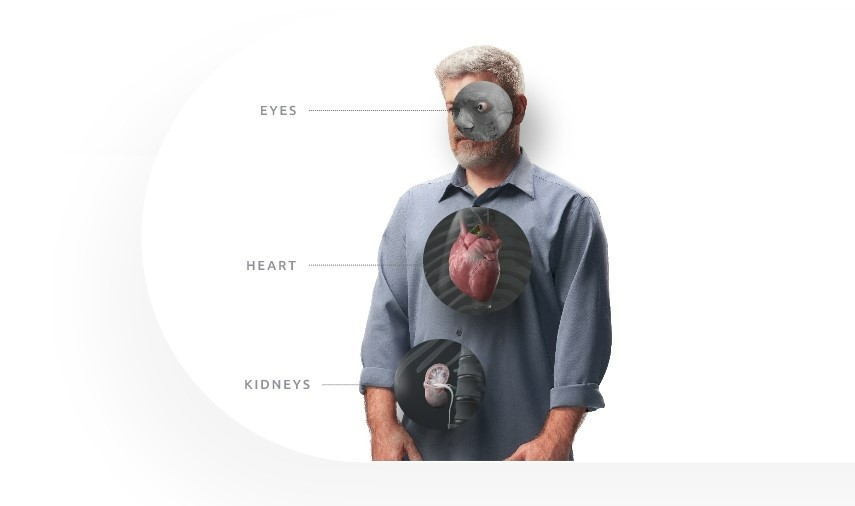
What organs does gout affect?
Is gout related to heart disease?
Uric acid is a risk marker for coronary heart disease (CHD)5-7
And is also a durable independent marker of risk for the development of hypertension5-7
- A meta-analysis of 9 studies with 25,229 patients with confirmed or suspected CHD suggested there was a ~2x greater risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with high sUA compared to patients with low sUA levels8
- The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for cardiovascular disease risk is 1.49 (95% CI, 1.43-1.56) in gout patients compared to nongout patients9
- Gout patients were shown to be at 50% greater risk of coronary artery disease (per data from an analysis of 70,000 patients)9
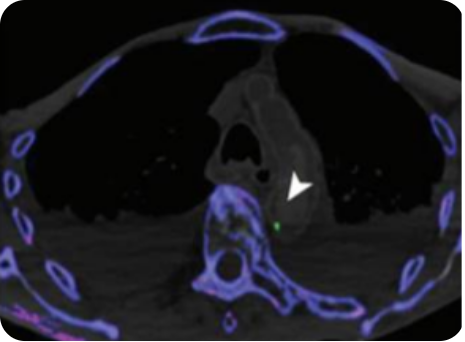
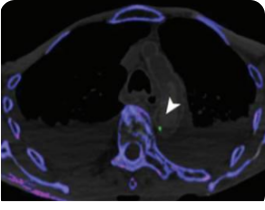
DECT scan: urate crystal deposition in the wall of the aortic arch.
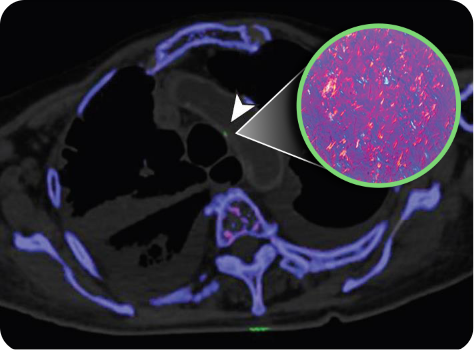
DECT scan: urate crystal deposition in the wall of the aortic arch.
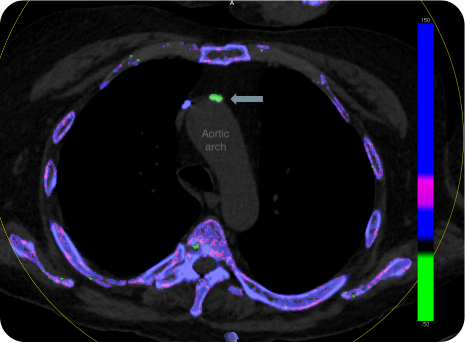
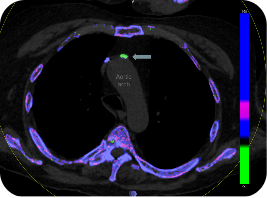
DECT scan: urate crystal deposition in the wall of the aortic arch.
In this vodcast, learn about potential
dangers of urate deposition in the heart
Is gout related to kidney disease?
Gout has been shown to be an independent risk factor for the onset and progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD)6,10,11
- Patients with gout and sUA of >7 mg/dL had a 43% higher risk of kidney disease than patients with gout who had lower sUA levels (HR, 1.43: 95% CI, 1.20-1.70)12
- Patients with hyperuricemia are at higher risk for acute kidney injury (AKI). Episodes of AKI have been associated with CKD13
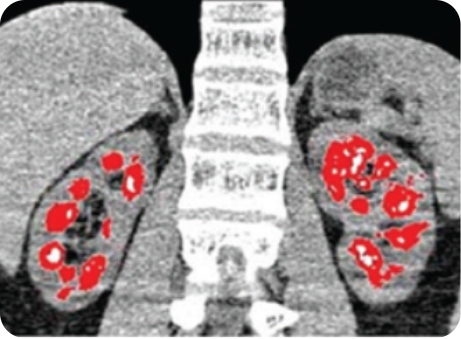
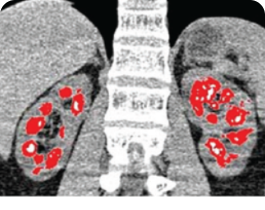
DECT scan: red dots represent urate crystal deposition in the renal medulla.
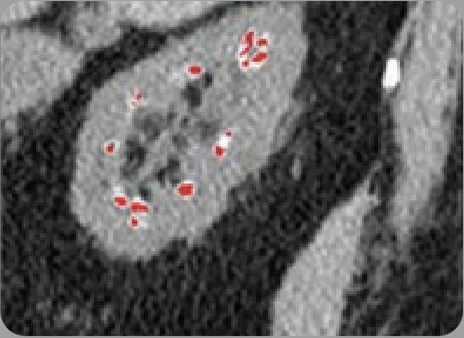
DECT scan: red dots represent urate crystal deposition in the renal medulla.
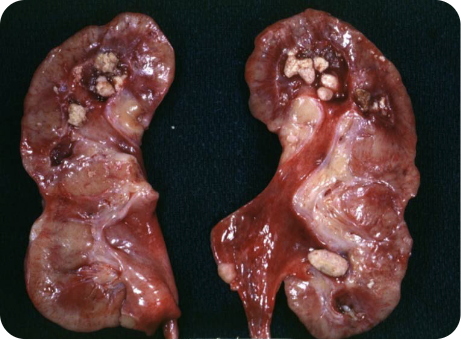
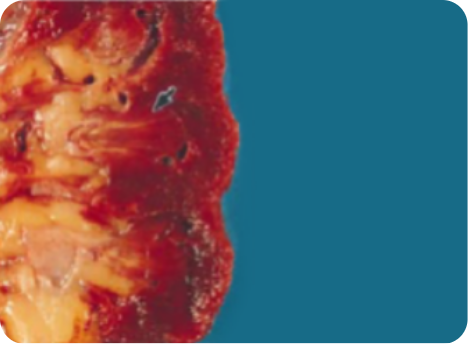
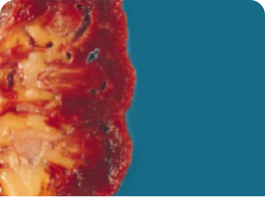
Renal stones in the collecting system of the kidneys.
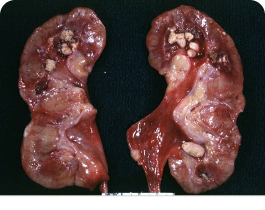
Renal urate deposits as thin yellow streaks within the renal medulla.
Watch “Urate in the kidneys? No kidding!”
Does gout affect the eyes?
Urate deposition in the eye15
Patients with long-term gout for more than 5 years were found to have twice the prevalence of dilated and tortuous blood vessels versus nongout patients16*
Urate crystal deposition has been observed in almost all ocular and adnexal locations, including17:
- Eyelid
- Conjunctiva
- Sclera
- Cornea
- Lens
- Iris
- Orbit
- Vitreous chamber
- Optic disk
- Retina
*Based on a study of 380 gout patients.
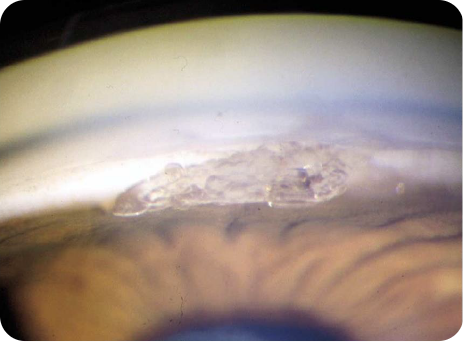
Coronal urate crystal deposition in the cornea and superficial
sclera of the eye.

Coronal urate crystal deposition in the cornea and superficial
sclera of the eye.
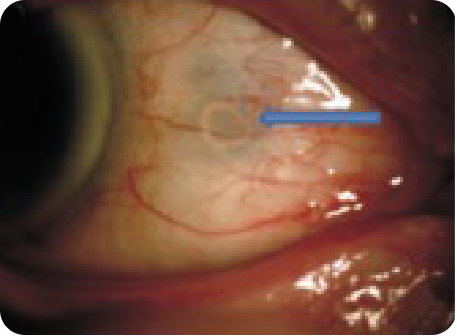
Urate crystal deposition on the iris and anterior chamber
of the left eye.
In this vodcast, learn what can result from
urate deposition in the eyes
Learn more about urate deposition in the bones